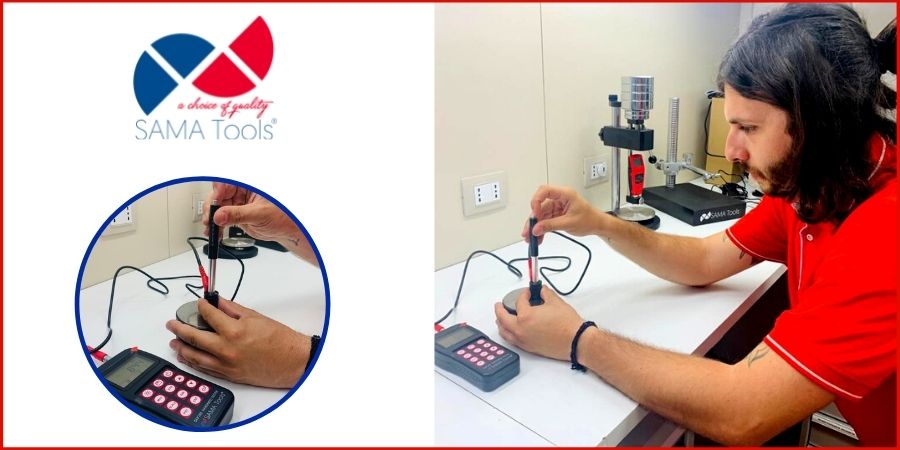
In the precision machining industry, there are a good number of aspects to consider in order to achieve the best possible results. Otherwise…
Posts
In a survey among LinkedIn users, we asked different professionals whether they used hardness testers in their line of work.
We received 126 answers as described here below:
44% YES
23% NO
33% used them in the past.
Of course, hardness testers are not all the same. And each one is suitable for a specific application. We invite you to keep reading to learn more about these non-destructive testing instruments.Click here to check the Linkedin poll.

Photo by www.canva.com
What are hardness testers?
According to the famous encyclopedia Britannica, a hardness tester is a “device that indicates the hardness of a material, usually by measuring the effect on its surface of a localized penetration by a standardized rounded or pointed indenter of diamond, carbide, or hard steel.”
Simply put, hardness testers are non-destructive testing instruments that allow you to determine, based on the applicable standard, the value of hardness of different materials, including, but not limited to:
- Steels and steel alloys
- Aluminum and aluminum alloys
- Brass
- Copper
- Plastic
- Thermoplastic elastomers

Photo by www.canva.com
How is hardness measured?
The typical hardness test involves an object called indenter which is pressed on and into the surface of the material being tested.
The indenter must have specific dimensions and must be loaded with a specific pressure depending on the type of tester.
Afterwards, the hardness is determined by measuring the depth of the penetration or the area of the indentation. Measuring one or the other will depend on the type of hardness test being performed. The most common ones include:
- Leeb hardness test
- Rockwell hardness test
- Vickers hardness test
- Brinell hardness test
- Shore hardness test
Why is hardness testing so important?
Knowing the hardness of the materials used on a piece or structure is important for various reasons. First of all, hardness testing allows you to assess important properties such as strength, ductility and wear resistance.
Therefore, with the information obtained, it is easy to determine whether the material is suitable for the application at hand or not and whether further surface treatment is necessary to achieve the desired results.
Also, it can be used to verify the quality of the material and determine if maintenance is required.
What are the different types of hardness testers?
As mentioned above, there are different hardness testers for different applications. So, let’s take a look at the most common ones.
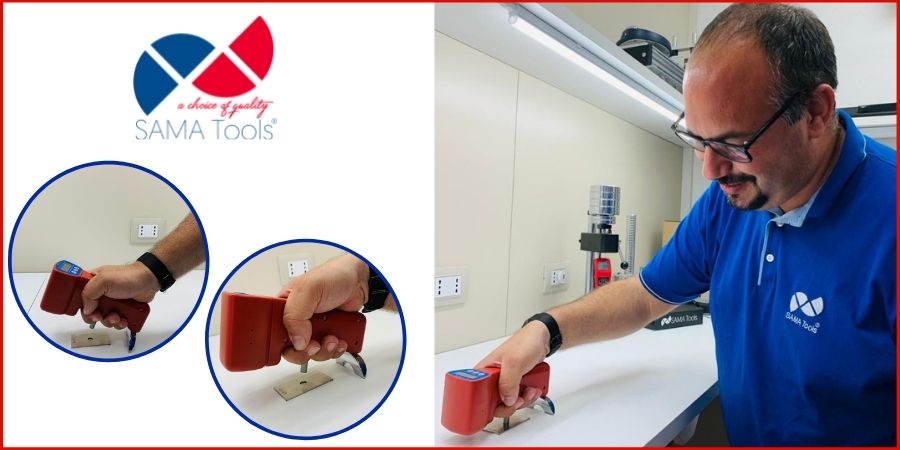
Leeb Hardness Testers
As the name suggests, these testers are based on the Leeb hardness test as defined in the ISO 16859 and ASTM A956 standards. It is a dynamic test method where the ratio of rebound velocity to impact velocity of a moving impact body is used to determine the hardness.
Leeb hardness testers are usually employed for testing various metals and alloys, and they are a great choice when checking incoming and outgoing goods, for quality control activities, and maintenance of structures and workpieces subject to wear.
Here at SAMA Tools, we offer 3 different Leeb hardness tester models :
- Leeb hardness tester SAP180, with D type impact probe and a test block.
- Touchscreen Leeb hardness tester SAP550, with touchscreen display and a wireless printer for printing reports on the go, which is great for quality control activities on the field.
- Pen type Leeb hardness tester SAP650, a compact and highly accurate tester with automatic detection of impact direction with a wireless interface.
Barcol Hardness Testers
Similar to the previous type, these instruments are named after the hardness test that they perform, the Barcol test.
This test is usually used on softer materials such as aluminum, aluminum alloys and some plastics. It was previously known as Barber-Colman Impressor since Walter Colman developed this test as a portable method during the World War II.
The process uses the indenter or “impressor” to press on the material and measure how deep the tip of it penetrates.
We offer 2 Barcol hardness tester models :
- Analogue Barcol hardness tester
- Digital Barcol hardness tester
Webster Hardness Testers
This simple model of hardness testers allows to measure the hardness of soft materials such as soft steels, aluminum, brass and copper. Moreover, it can be applied on different geometries and very small thickness values.
The values obtained can be easily converted to the common scales, including Vickers, Rockwell and Brinell.
We offer 3 versions of the Webster hardness tester:
- SAMW-20
- SAMW-20a
- SAMW-20b
The main difference is the range of thickness and diameter they can be applied on.
Shore Hardness Testers
Shore hardness is defined as the resistance of a material to penetration from a spring-loaded needle-like indenter.
By definition, we can easily conclude that the process to perform a hardness test with a Shore hardness tester is very similar to the one with the Barcol tester.
There are different scales for Shore testing, the most common ones being the Shore A scale for soft elastomers like rubber, and Shore D for hard elastomers and other polymers like thermoplastics and thermosets. This makes Shore hardness testers a great option for quality control activities in rubber and plastics industries and for maintenance on ring nuts and gaskets.
We offer 3 different versions of the Shore hardness testers:
- Analogue Shore Hardness Testers
- Digital Shore Hardness Testers
- Pro Digital Shore Hardness Testers
The last one in the list is the most powerful of all, since it can handle more than the two scales mentioned above, and it comes with many other interesting features.
We also offer special stands for more accurate and repeatable results, and Shore test blocks for verification and calibration purposes.
Bench Hardness Testers
The most specialized hardness testers in the market are usually bench hardness testers, since they offer a higher accuracy and repeatability. Therefore, they are the favorite option for metrological laboratories and applications which require the maximum of these two aspects.
These testers work with the indentation principle by applying a constant load over a specific period of time on an indenter which is in contact with the sample. They can use indenters of different sizes, shapes and materials, thus providing the possibility to work with different standards and scales with the same device.
We offer 5 versions of bench hardness testers, some of them are manually operated and others which are motorized. The versions are:
- SAB150-B which is manual, analogue and works with Rockwell A, B and C
- SAB150-BM which is motorized, analogue and works with Rockwell A, B and C
- SAB150-B/DGT which is manual, digital and works with Rockwell A, B and C
- SAB150-BM/DGT which is motorized, digital and works with Rockwell A, B and C
- SAB187,5-B which is motorized, analogue and works with Rockwell A, B and C, Brinell and Vickers hardness scales. It comes with a microscope.
All of our bench hardness testers come with a diamond cone indenter and corresponding test blocks.
So, which hardness tester is used the most?
According to the poll, most of the participants who claim to use it or have used it in the past, say they have used the bench hardness tester. This is followed by users of shore hardness testers and Leeb hardness testers. Last but not least are the Webster and Barcol hardness testers.
The most common answers to what it was used for:
- Inspection on workpieces after hardening to ensure durability.
- Controling of incoming goods.
- Recognizing the hardness of the material to be welded.

Photo by www.canva.com
How can I select the best hardness tester for my needs?
When selecting the best hardness tester for your needs, there are different things to consider. The most important are:
- Type of material tested
- Requirement of standard compliance
- Material’s approximate hardness
- Sample size and geometry
- Mounting requirement
- Number of samples to be tested
- Required accuracy and repeatability

Photo by www.canva.com
If you want to see all the hardness testers that we offer and select the right one for your needs, just click here.
Instead, if you are not sure yet or have any doubts about hardness testers, we recommend you contact us and one of our specialists will gladly assist you.
Video summary: Portable or bench hardness testers? The challenge
Based on the name “ultrasonic instruments”, it is clear that these are devices that use ultrasound to perform their function. So, to be able to answer the question “what are ultrasonic instruments?” , one should begin by describing what ultrasound is.
What is ultrasound?
Ultrasound makes reference to the principle of using sound waves at very high frequencies, usually higher than those the humans can hear. This means that ultrasound applies frequencies higher than 20 kilohertz with operating values reaching up to the gigahertz ranges depending on the ultrasonic instrument.
The word ultrasound is commonly heard in the health sector, where ultrasound imaging is commonplace.
Yet, when it comes to the engineering field, ultrasonic instruments are used for different purposes, such as non-destructive testing, measurement and quality control.
Ultrasonic instruments for non-destructive testing
Some ultrasonic instruments are used for non-destructive testing in order to identify and verify mechanical features while keeping the integrity of the part tested.
This type of ultrasonic instruments is especially useful for finished parts or products. They allow you to identify and test aspects such as:
- Flaws on the surface finish which may not be visible to the eye.
- Hardness of the material.
- Pipe fractures that may lead to leakage.
- Other invisible flaws.
Using ultrasonic instruments for non-destructive testing provides you with a series of advantages, for example:
- Both internal and external flaws can be detected.
- Both volumetric and crack like flaws can be detected no matter their orientation
- Some instruments take the exact same time to test pieces with different thickness.
- The radiation risk present with the radiography method of testing is eliminated.
Among the most common ultrasonic instruments used for non-destructive testing, we offer:
- Ultrasonic flaw detector – SAFD500
- Ultrasonic flaw detector – SAFD660
- Ultrasonic hardness tester UCI method – SA459C
Reference standards for non-destructive testing
Non-destructive testing is regulated by different standards which determine the verification methods to be applied according to the material, the thickness of the metal, the type of joint, etc.
S.A.M.A. Italia is associated with UNI Ente italiano di Normazione:
Being a Member allows you to participate personally in the definition of the rules, helping to define the rules of your sector of reference rather than subject them.
UNI allows members and not to consult the reference standards at any time, purchasing them online.
Italian Association of Non-Destructive Tests
AIPnD has been present in Italy since 1979. It’s a scientific, cultural and professional organization and it’s among the first and most important in the world in its sector.
Its members belong to institutes, research centers, organizations, schools, professional firms, instrumentation manufacturers and companies that provide PnD services.
The association is based in Brescia, Italy and promotes scientific and technical knowledge. It’s also involved in the technological development of non-destructive tests as well as enhancing the profession of those working in the sector.
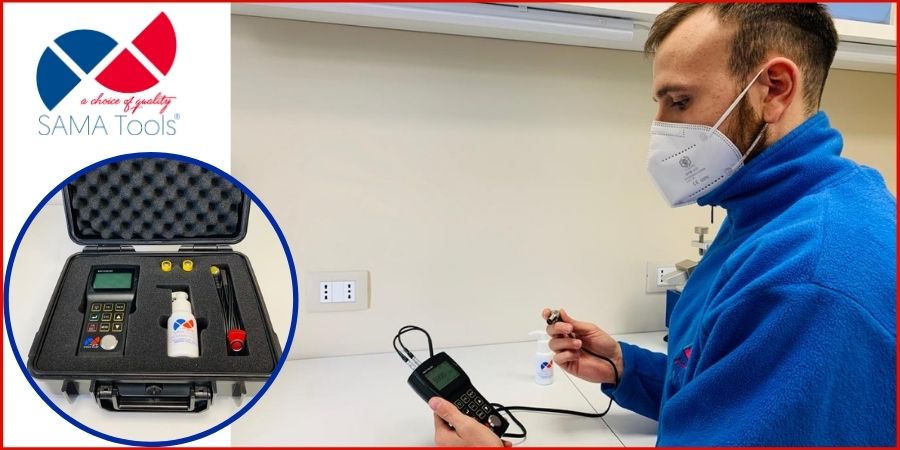
Ultrasonic instruments for measurement
Another group of ultrasonic instruments is formed by those used to measure parameters such as the thickness of a material or a coating with high precision.
This group uses a measuring method called “Ultrasonic Thickness Measurement” or UTM. Therefore, they are usually known as ultrasonic measuring gauges.
Ultrasonic measuring gauges are capable of measuring the thickness by using a probe that generates an ultrasound pulse and sends it through the thickness of the part being measured.
Then, the instrument calculates the thickness by a calculation that considers the time needed for that ultrasound pulse to go through, get reflected by the opposite surface of the piece and return to the probe.
With the values obtained by the instrument, it is possible to identify and verify:
- Thickness of the material for possible wear.
- Corrosion on the material.
- Possibility of splitting material.
- Accurate coating thickness.
Considered part of the non-destructive testing tools, ultrasonic instruments for measurement offer a variety of benefits, such as:
- Not damaging the measured sample.
- Access to both sides of the sample is not required.
- High precision achieved.
- Do not require laboratory like conditions to work.
- These instruments are cheap compared to other alternatives.
Some ultrasonic measurement instruments that you can get with us include:
- Precision ultrasonic thickness gauge – SAUT160
- Graphic ultrasonic thickness gauge – SAUT500D-SW
- High accuracy ultrasonic thickness gauge – SAUT350-SW
- Through coating ultrasonic thickness gauge – SAUT310D-SW
- Ultrasonic thickness gauge – SA8812
Watch the video we made on the graphic thickness gauge
Ultrasonic instruments for quality control
Both non-destructive testing and measurements are used to compare results with what is expected. If results match the specifications of the part or the product tested, it can be concluded that the part has the quality desired.
It is then obvious that ultrasonic instruments are an important asset for quality control. Most ultrasonic instruments provide information which is essential for quality assurance, such as:
- Roughness measure and control.
- Wall thickness.
- Coating thickness.
- Color and gloss differences measure.
- Hardness of the material.
Therefore, benefits for the quality control department include all the benefits mentioned above, plus the fact that some of these instruments can be applied directly in the production line without the need of taking samples to a laboratory.
Also, all the ultrasonic instruments mentioned above are useful for quality control activities, but we have more. Other instruments we offer and can come in handy for quality control are:
- Portable surface roughness testers.
- External probe surface roughness testers.
- Integrated probe digital coating thickness gauges.
- External probe digital coating thickness gauges.
And this is just a small list.
What materials can be tested?
At this point, you should already known what are ultrasonic instruments, how they work and their main applications.
However, it is also important to understand which are the materials that make ultrasonic instruments the right choice.
Fortunately, these instruments work with a wide range of materials, especially if they are high-quality instruments.
For example, our precision ultrasonic thickness gauge – SAUT160 can measure the thickness of ultrasonic conducting materials such as:
- Steel
- Cast Iron
- Aluminum
- Copper
- Brass
- Zinc
- Quartz Glass
- Polyethylene
- PVC
- Gray Cast Iron
- Spheroidal Iron
8 Articles on ultrasonic instruments for further information
Are you interested in learning more about this topic?
We have selected these themed articles for you:
1. Ultrasonic Thickness Measurement: definitive guide
2. Coating Thickness Measurement
3. Graphic Ultrasonic Thickness Gauge – SAUT6100D-SW
4. Sheet Metal Manufactoring and Quality Control
5. Industrial Pumps: What checks do you need to do for high performance?
6. Quality Control of the Coating on Commercial Vessels and Mega Yachts: MCR Marine
7. Ultrasonic Thickness Gauge: the case of Progetto PSC S.r.l
8. Gloss vs Brightness: What’s the difference?
Final thoughts
It is clear that a short and accurate answer for the question “what are ultrasonic instruments?” could be “powerful measuring and testing tools”.
The fact that these instruments are capable of providing essential information to improve the quality of products and processes makes them a must have for any company, that takes their business seriously.
Keep in mind that ultrasonic instruments are not only for quality control, some of them are also very useful on the field to perform maintenance inspections on tanks, metal sheets, pipelines, under pressure containers, bulkheads, and other equipment where corrosion and other defects may be present.
If you are interested in acquiring any of our ultrasonic instruments, or you have any inquiries about these and any other of our products or services, do not hesitate to contact us. We are happy to help you.